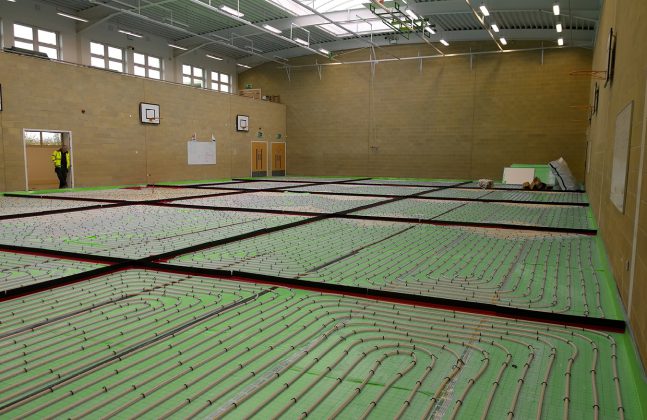
Did you see our last post on choosing the right UFH system for you? We explored the various different options of underfloor heating, from “In-Screed” and “Dry Fit” systems to “Electric” systems. This time we look at the extra measures to take to avoid the risk of floor failure.
Floor failure can come in many forms, from floor coverings de-bonding to excessive screed cracking and while it is not always clear, there is always a specific reason for why the failure has occurred. A major reason can often be due to the fact that one contractor provides the heating system, with another providing the screed and a third the floor coating. The best solutions combine all these elements to a single point of responsibility, which can effectively mitigate the risk associated with them.
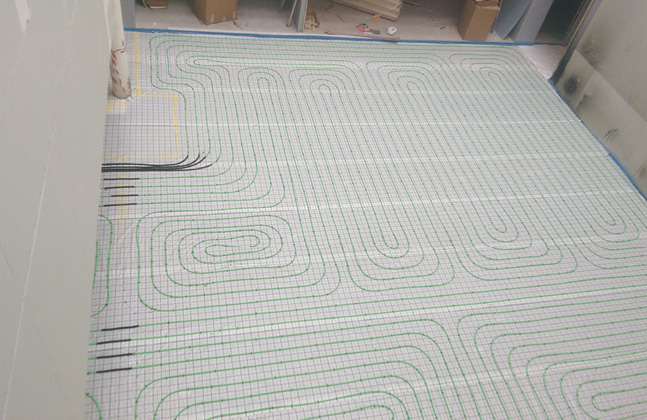

Underfloor heating single-source build ups means that each component has been designed to work together
Luckily, single-source floor build-ups are available, in which each element has been specifically designed to work together. When considering UFH system design, for example, the floor covering selection can have a huge impact on the UFH system’s performance and outputs. This is due to the fact that as floor covering resistance increases, the UFH system efficiency will reduce. For this reason the system specification must be bespoke for each facility and requirement.
Suitable Screed Types
Similar to the choice of UFH system type, the screed type must also be carefully selected based on the specific building and programme requirements. Some key considerations specific to UFH within screed are:
1.Floorzone Depth
One of the important considerations should be how much depth there is before selecting a screed and UFH system. Most new builds will allow a typical 150mm zone which lends itself nicely to a specification of 50mm insulation and 70-100mm of screed. Where this zone is reduced, typically for renovation/refurbishment projects, then a product such as cementitious, pumped self-levelling screed should be specified.
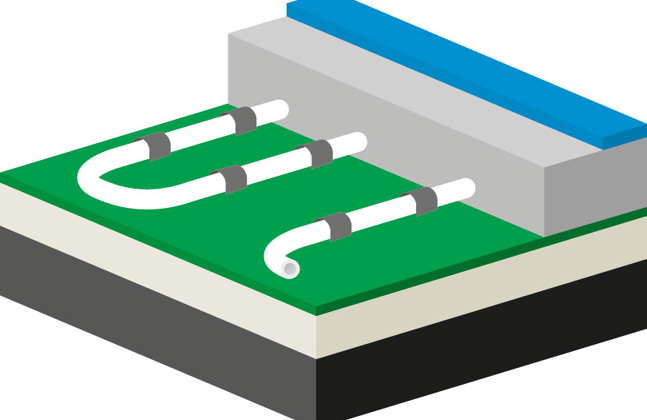
Substrate (black), insulation board (white), pipework set into the (grey) floor screed and finally (blue) floor finish
2.Structural Movement Joints
Where structural joints are shown, it is important to mirror this in the UFH and screed design. Where possible the UFH pipes should not cross building movement joints as this movement can shear the pipes.
If it is not possible to avoid crossing these joints, then it is important that the UFH pipes are protected sufficiently to allow for this movement.
3.Expansion Joints
Although it is not necessary to protect the UFH pipes in the same way as with a structural joint, it is nevertheless advisable to be aware of expansion joints within the screed, especially if there are unheated areas.
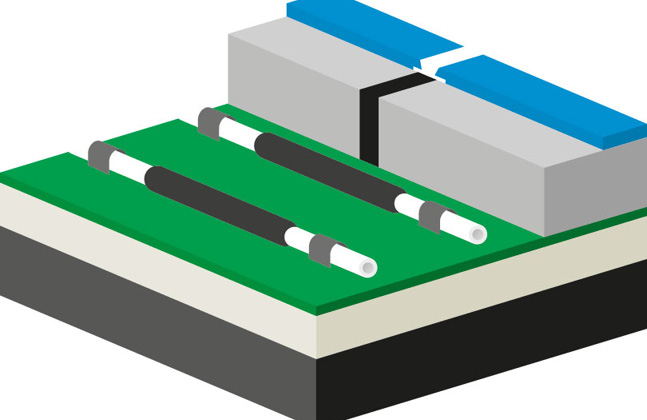
A typical expansion joint is shown here
4. Adjoining heated areas
If the difference in temperature is large enough, this can cause thermal shock, ultimately resulting in cracks in the screed. Here a thermal break and expansion would be required to avoid floor failure here.
5. Temperature
There needs to be careful management of floor surface temperatures to ensure that surface temperatures do not exceed the specified maximum, which is generally around 29°C for most types, but is reduced to 27°C for sensitive flooring materials such as timber or vinyl.
The floor finish and screed type have an inherent temperature resistance which needs to be accounted for when designing the system, for example liquid screeds have a typical thermal conductivity of 1.9 W/mK whereas sand and cement types are closer to 1.2 W/mK. This means that it is important that the specified screed type is not changed on site, as this can significantly affect the UFH outputs and performance.
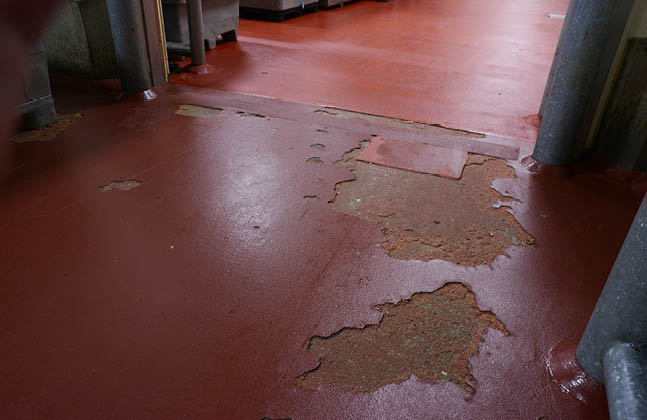

Floor failure can lead to costly repairs and refurbishments
6. Heat Up Cycle & Commissioning
Screeds with UFH must be commissioned prior to laying floor coverings, as any moisture within the screed cannot be released properly once floor coverings have been laid, which in turn can lead to expensive failure of the floor covering. The heat-up cycle should follow BSEN 1264 and BSEN 8204 guidelines.

If you would like any further information on underfloor heating systems and the necessary considerations when specifying this type of flooring, leave a comment below or drop us a line, we’d be happy to help.





